Published 2025-09-07.
Last modified 2025-10-27.
Time to read: 8 minutes.
llm collection.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that helps AI systems connect to external data and tools.
Abbreviated History
Anthropic created the MCP as an open-source framework in November 2024. Within 6 months, MCP had become commonly used technology. Its purpose is to standardize the way artificial intelligence (AI) systems like large language models (LLMs) integrate and share data with external tools, systems, and data sources.
Version 1.3.0 of the mcp Python SDK for the Model Context Protocol was
released on PyPI on February 20, 2025. This version did not introduce breaking
changes on its own, but it was superseded on March 26, 2025, by a major
Model Context Protocol (MCP) specification
update that did. The result is that the mcp v1.3.0 package
became incompatible with the modern MCP ecosystem due to the changes in later
versions of the specification. The breaking changes were:
- The earlier 2024-11-05 specification relied on HTTP with Server-Sent Events (SSE) for streaming data from server to client. The 2025-03-26 update replaced this with the Streamable HTTP transport that supports bidirectional streaming over a single connection. This meant clients and servers built for the older SSE model could not communicate with those running the new Streamable HTTP transport. Since then, many clients implemented support for both streaming standards.
- The earlier 2024-11-05 specification had a less standardized authorization process. The 2025-03-26 version adopted the OAuth 2.1 authorization framework. This meant that older clients could no longer authenticate correctly with up-to-date servers.
- The 2025-03-26 update introduced the ability to batch multiple JSON-RPC calls, which improved efficiency for complex workflows. However, its removal in the 2025-06-18 version of the MCP specification caused a new round of incompatibility. This latest version of the MCP specification tightened security considerably at the expense of compatibility with existing implementations.
The official mcp Python SDK on PyPI is frequently updated to
implement the latest MCP specification, which at the time of writing this
article was 2025-06-18.
The latest version of the mcp Python SDK on PyPI is 1.14.1,
released on September 18, 2025. This SDK version is compatible with and
implements the features of the 2025-06-18 MCP specification. It is currently the
recommended version for developers building clients and servers with Python.
Contrary to the hype of today (2025-10-27):
- MCP is not easy to work with.
- Most current MCP implementations are quite insecure.
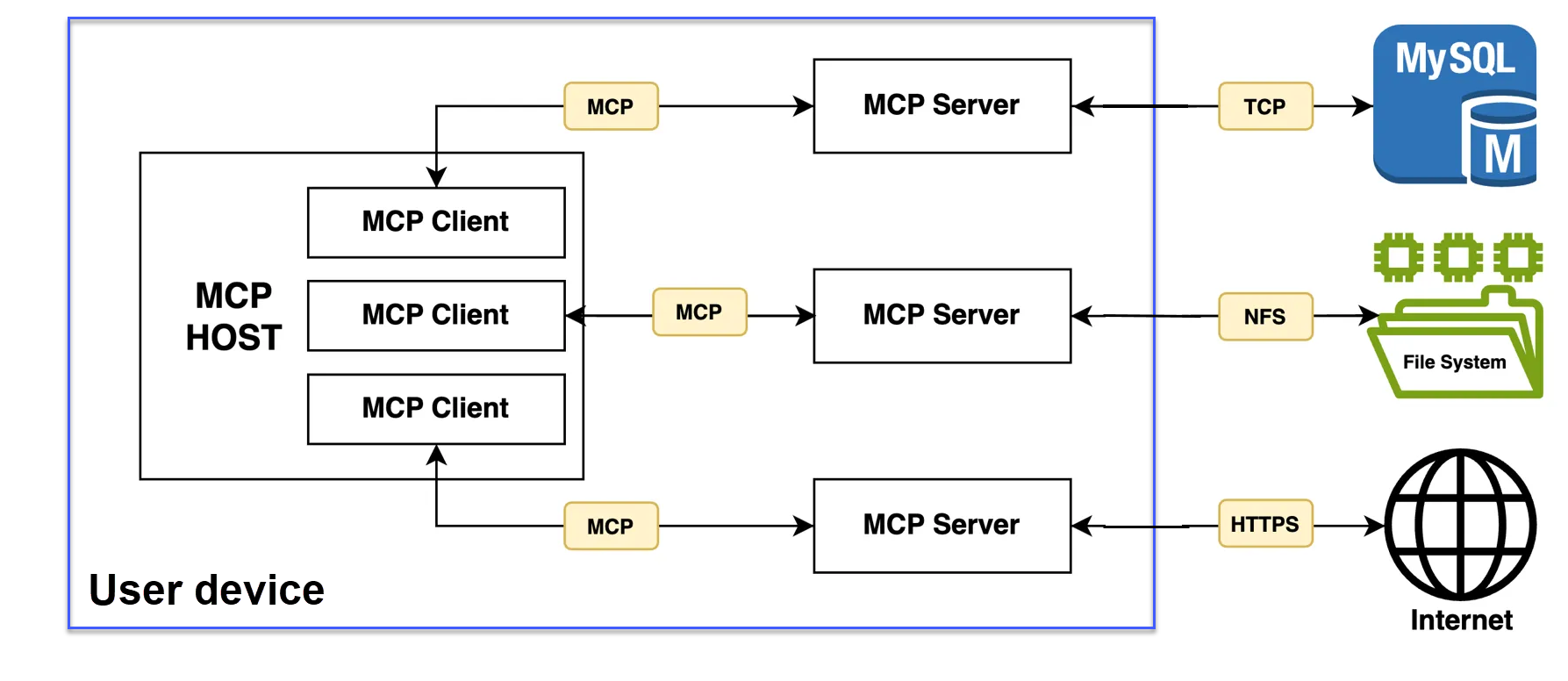
MCP Components
Some important components of the MCP architecture include hosts, clients, and servers.
MCP Hosts
An MCP host is the user-facing application that coordinates and manages one or more internal MCP clients on behalf of the user. Hosts initiate connections to MCP servers and orchestrate the overall flow between user requests, LLM processing, and external tools. MCP hosts include:
- AnythingLLM, a desktop application that allows users to chat with documents and use AI agents.
- Claude Desktop
- Cursor.
- Custom applications built using libraries like LangChain, smolagents, and the Hugging Face Python SDK
-
The MCP SuperAssistant Extension was created to bridge the gap between AI platforms like
ChatGPT,
DeepSeek,
Google Gemini,
GitHub Copilot,
Google AI Studio,
Kimi,
Grok,
OpenRouter,
Mistral,
Perplexity,
T3 Chat,
Qwen,
Z,
and the MCP tools.
MCP SuperAssistant makes a Google Chrome plugin. Other browsers (works with Chrome, Firefox, and other Chromium-based browsers like Edge, Brave, and Arc) Click the Add to Firefox button
While these AI platforms are powerful for general knowledge and reasoning, they lack the ability to execute specific tools or access external systems directly. This extension solves that problem by providing a seamless way to detect, execute, and integrate MCP tools within these platforms.
Installation and setup - LM Studio
- Visual Studio Code
MCP Clients
MCP clients send requests to MCP servers and return the result to the MCP host. Clients reside within the host application and manage communication with a specific MCP server. They provide servers with access to files, database connections, provide API integrations, and other contextual services. MCP clients can access local services or remote servers.
For Ollama:
- MCP ToolSpec
- LlamaIndex + MCP Usage
- llamacloud-mcp
r/LocalLLaMAmcp-openai-gemini-llama-example- More...
MCP Servers
MCP servers are external programs or services that expose capabilities such as tools, resources, and prompts via the MCP protocol. MCP servers connect LLMs to the outside world, dramatically expanding what LLMs can do for users.
Claude was the first LLM to get an MCP server because Anthropic, the developer of Claude, also initiated MCP. Not to be outdone, OpenAI also offers MCP support for ChatGPT:
- Building MCP servers for ChatGPT and API integrations
- ChatGPT Developer mode
- GitHub MCP Registry
- Remote GitHub MCP Server
- PostgreSQL Model Context Protocol (PG-MCP) Server
Le Chat, by Mistral, provides many MCP connectors. BTW, Mistral does not force slow typing on users; it blasts responses to you instead.
Many MCP servers are built using Node.js,
for example, GitHub Copilot and Azure DevOps MCP servers,
and those distributed as npm packages.
This aligns well with Visual Studio Code’s ecosystem.
Note that Cursor is just a customized version of Visual Studio Code.
For example, the File System MCP server and others mentioned in guides for
setting up MCP servers in Visual Studio Code
often use Node.js for operations like file management or API interactions.
The npx (Node Package Execute) command,
which requires Node.js, is frequently used to run these servers.
npx is used to run a command from a local or remote npm package.
I wrote about npm in Node.js, NVM, NPM and Yarn.
If the package containing the command to be executed is not available locally,
it is automatically downloaded.
npx is bundled with npm versions 5.2.0 and higher.
Before configuring MCP servers, ensure you have Node.js installed on your
system with npx available for package execution.
Most MCP servers require the Node.js runtime environment for proper functionality.
A better approach, taken by some MCP servers, is to be bundled as Visual Studio Code extensions, where they run in the extension host process, bypassing the need for Node.js. The extension host is a Node.js process that runs extension code. Support for MCP servers running as Extension Host processes started with Visual Studio Code version v1.101 (May 2025).
Warning: npm and npx are
security nightmares.
PyPi is no better,
and I do not believe uvx improves the situation.
Just be aware that the glue used by MCP servers to interact with LLMs is an unconscionable security hazard.
If you have sensitive information, run everything locally on an air-gapped machine.
Yes, security vulnerabilities really are that bad.
MCP Tools
MCP tools enable models to interact with external systems, such as querying databases, calling APIs, or performing computations. Each tool is uniquely identified by a name and includes metadata describing its schema. MCP tools are model-controlled, meaning that the LLM can discover and invoke tools automatically based on its contextual understanding and user prompts.
Erroneous Information
modelcontextprotocol.io was the only information source that did not have glaring factual errors
that I found while researching this article.
Even the most visible documentation from the originators of the technology had fundamental factual errors.
But verify.
From OpenAI and Google
During the week I was writing this article (early September 2025), ChatGPT (GPT5), Google Gemini, and Google Search all confidently described Cursor as an MCP client and cited incorrect reasoning.
I can see why the confusion happened: the List of Claude MCP Clients contains these same mistakes. Ignore that web page. I see many websites confusing the MCP host and MCP client roles, even many websites that should be expected to be authoritative.
Cursor is actually an MCP host that contains many MCP clients.
Grok did not make that mistake, but sometimes it expanded MCP to Microsoft Code Push, which was erroneous.
From Software Documentation
Visual Studio Code documentation often is unclear about whether stated facts apply to a workspace or a project. The capabilities of Visual Studio Code have changed recently. As a result, many people use the terms “project” and “workspace” interchangeably. Loose definitions result in vagueness, which is often confusing and not actionable.
cannot be trusted
Quotes are often used in an article when the author wants to refer to what someone else said without accepting the veracity of the other party’s statements. I made no attempt to correct any misuse of Visual Studio Code terms “project” and “workspace.”
Security
MCP is insecure by default
Not only are the Python and Node.js ecosystems security nightmares, but MCP implementations are all too often unacknowledged security risks themselves.
This post covers the biggest risks (with real examples) and how to think about MCP securely:
- Tool Description Injection is real. Malicious tool descriptions can silently inject harmful prompts. Your agent can be tricked before it even starts executing.
- The authentication situation is not great. OAuth is often skipped or poorly implemented. Many public MCP servers don't verify requests or protect user sessions. Some even accept unauthenticated calls.
- Supply Chain Risk is underestimated. Most people install MCP packages (npm, Docker) without realising how easily they can be tampered with. One poisoned update can lead to dangerous results.
- Real-world security failures have already happened. Like hundreds of exposed servers on 0.0.0.0 with command-execution flaws, the Supabase MCP Lethal Trifecta Attack, Asana Data leak, MCP-Remote Command Injection, and accessing private repositories via GitHub MCP.
- The latest spec introduces security best practices like no token passthrough and enforced user consent. But most implementations simply ignore them.
See also:
- The MCP Authorization Spec Is... a Mess for Enterprise
- MCP Security Best Practices
- Best Current Practice for OAuth 2.0 Security
Every MCP connection is a potential attack surface
Setting Up MCP Servers
For Windows computers, MCP servers can be installed as native Windows processes or as WSL processes. Install in one or both OSes as appropriate.
Linux:
Elsewhere, define these environment variables:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="AKIAxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION="us-east-1"
$ source ~/.bashrc
Native Windows: Define these environment variables for the current user:
setx AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID AKIAxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx setx AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx setx AWS_DEFAULT_REGION us-east-1
Note that setx breaks PATHs longer than 1024
characters. See Add To Windows User Path for a better way to add a
directory to the user PATH.
MCP File System
The following shows how to install on native Windows:
$ npx @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem c: e: m: n: o: u: Need to install the following packages: @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem@2025.8.21 Ok to proceed? (y) Usage: mcp-server-filesystem [allowed-directory] [additional-directories...] Note: Allowed directories can be provided via: 1. Command-line arguments (shown above) 2. MCP roots protocol (if client supports it) At least one directory must be provided by EITHER method for the server to operate. Secure MCP Filesystem Server running on stdio Started without allowed directories - waiting for client to provide roots via MCP protocol
The following shows how to install on WSL using matching file systems:
$ npx @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem \ /etc /media /proc /run /sys /usr /home /opt /root /tmp /var \ /mnt/c /mnt/e /mnt/f /mnt/m /mnt/n Need to install the following packages: @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem@2025.8.21 Ok to proceed? (y) Usage: mcp-server-filesystem [allowed-directory] [additional-directories...] Note: Allowed directories can be provided via: 1. Command-line arguments (shown above) 2. MCP roots protocol (if client supports it) At least one directory must be provided by EITHER method for the server to operate. Secure MCP Filesystem Server running on stdio Started without allowed directories - waiting for client to provide roots via MCP protocol
Resources
- My article: Visual Studio Code Extension Host MCP Servers
- My article: Options for Controlling Ableton Live with MCP
- Book: Model Context Protocol: Advanced AI Agents for Beginners by Mehul Gupta and Niladri Sen.
-
r/mcp - MCP Course: Key Concepts and Terminology
- Build and deploy Remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers to Cloudflare
-
https://mcpservers.orgis a collection of MCP clients and servers. There were 1968 MCP servers listed on 2025-09-06, and several dozen clients listed. Surprisingly, the website has no search capability. - MCPJam Inspector, an MCP server testing tool.
- MCPHub: The Unified Hub for Model Context Protocol (MCP) Servers
-
OpenAI Connectors and MCP Servers
This is a great resource: Using MCP with OpenAI & MCP Servers - Grok MCP Plugin provides chat, image understanding, and function calling. This plugin is not packaged; so you must clone and build the project yourself.
- Awesome Remote MCP Servers
- Codename Goose, an open-source, extensible AI agent for automating engineering tasks.
- Flowise for visually building AI agents.
- Stop Converting OpenAPI Specs Into MCP Servers
- MCPJungle
- MCP Personas
-
test-mcp, an automated testing tool for MCP servers and agents. - Omnimesh AI Gateway, an API gateway that provides authentication, logging, rate limiting, server discovery, and multi-protocol transport support.
-
mcp-server-dump, a command-line tool to extract and document MCP server capabilities, tools, resources, and prompts in various formats. - Dexto, an orchestration layer for AI agents. Connect your models, tools, and data into a smart interface to create agentic apps.
- Introducing gpt-realtime and Realtime API updates for production voice agents